
- Home
- Maintaining Independence and Safety in the Home
- Addressing Ageism and Promoting Positive Attitudes Towards Aging
- Estate Planning: A Simple Guide for Seniors
- Rediscovering Your Inner Innovator: Thinking Outside the Box
- How Seniors Might Celebrate Milestones
- Cherishing Our Seniors: 6 Ways to Show You Care
- Nourishing the Golden Years: 5 Dietary Considerations for Seniors
- The Importance of Preventive Care and Regular Check-ups for Seniors
- Adapting to Change
- Feeling Lost in a Sea of Doctors and Deductibles
- Live Your Best Life: Easy Exercises for a Healthier, Happier You
- God's Gifts in the Digital Age: Technology Enriching the Golden Years
- Living Well with Arthritis: A Guide to Natural Approaches
- Helping Seniors Combat Loneliness and Thrive
- A Senior’s Guide to Weight Loss
- Ready for Your Next Chapter? A Friendly Guide to Retirement Planning
- Embrace Aging with Delicious Food: Your Guide to an Anti-Aging Diet
- BMI and Seniors: Understanding the Numbers for a Healthier You
- Finding Freedom from Regret: A Christian Perspective for Seniors
- How Seniors Benefit from Drinking Water
- Finding Peace and Contentment in Knowing Jesus: A Guide for Seniors
- 5 Ways for Seniors to Make Meaningful Connections
- Finding Freedom from Guilt
- How Seniors Can Help When Disasters Occur
- A Senior's Guide to a Mindful Morning Routine
- Strength Training for Seniors
- The Inspirational Journey of Colonel Sanders"
- Boosting Vitality and Longevity for Seniors
- Boosting Senior Health: A Guide to Antioxidant-Rich Foods
- Engaging Ways for Seniors to Foster Intellectual Growth
- A Biography
- Strategic Estate Planning for Family Harmony
- Navigating the Challenges of Aging with Grace and Humor
- Decoding the Nostalgic Humor in Senior Citizen Phrases
- Senior Driving: When to Hit the Brakes
- Seniors: Guiding the Younger Generation
- Medications & Herbs: A Risky Recipe
- Preserving Your Legacy
- Balancing Act
- Seniors Need Rest Too
- Helping Someone Survive an Emergency
- The Pros and Cons of Perseverance
- You Can Experience Joy
- Dealing with Difficult Emotions
- The Best Time to Retire
- How to Declutter Your Home
- Benefits of Adequate Sleep
- Encouraging an Adult Child
- Maintain and Improve Your Brain Power
- How to Deal with Embarrassment
- When You’re Beyond the End of Your Rope
- Help a Struggling Friend
- Taking Care of Yourself
- Improve Your Concentration and Focus
- How the Web Impacts Your Life
- Your Personal Power
- On Building and Maintaining Relationships
- A Picture of God
- Becoming More Adaptable and Resilient
- Making the Best of Bad Situations
- The Surprising Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
- Cultivate an Attitude of Gratitude
- Repair a Relationship
- AVOID CAREGIVER BURNOUT
- Top Tips for Keeping a Sharp Mind
- Succeed in Social Gatherings
- Benefit Society Even in Retirement
- Surviving Winter
- From the Depths of my Scatter-Brained Mind
- The Story of Joseph
- Parenting is Not for the Faint-hearted
- Keeping Passion in Your Marriage
- The Bible’s Influence on History
- Surviving the Loss of Your Spouse
- Purposeful Traveling
- Senior Money Management
- When Life Goes South
- Retire Well
- Using Smartphones and Tablet
- How to Choose an Assisted Living Community
- Giving and Getting Help
- Avoid Being Scammed
- Senior Safety Source
- Technology Can Benefit Seniors
- Why Do We Dream
- Your Mental Ability
- What Is Cold Water Therapy?
- Plan a Road Trip
- Comparing Sweeteners
- Improve Your Communication Skills
- Being Comfortable in Social Gatherings
- Store-Bought vs Home-Grown Food
- Surviving Tough Times
- What About Social Media?
- What About Intermittent Fasting?
- Combat Mental Fatigue
- Be Alone and Don’t Feel Lonely
- Building and Maintaining Relationships as We Age
- Being True to Yourself and Others
- Remaining Generous in a Difficult Economy
- How To Stay Awake After A Poor Night’s Sleep
- Stay Warm in the Winter
- Dealing With Insufficient Retirement
- Seniors Can Avoid Fraud
- An Attitude of Gratitude
- Ways to Make Your Friend Feel Appreciated
- 9 Ways Tackling Clutter Can Enhance Your Wellbeing
- Biofeedback: Is It Right For You?
- A Biblical Admonition
- Debunking 5 Myths About Caregivers
- Fun Activities for Your Elderly Parents
- Considered Getting a Pet?
- The Art of Grandparenting
- Seniors Aging Gracefully
- Travel Destinations in the Continental U.S.
- Micro Exercises for Senirs
- The Great Sport of Pickleball
- Helping Someone with Alzheimer's
- The Positive Side of Adult ADHD
- Still Fresh, Ancient Wisdom
- Dealing with Memory Issues
- Considerations for a Retirement Home
- Know About Panic Attacks
- Improving Sleep
- 4 Comforting to Help You Cope with Grief
- Exercise Safely with Back Pain
- Food Allergies And Intolerances
- Loneliness and Your Health
- What Jaws Can Teach You About Overcoming Fear
- Simple Tricks to Beat Brain Fog
- How Focus Can Change Your Life
- 5 Ways To Build Your Resilience
- Overhaul Your Diet In Six Simple Steps
- Handling Social Anxiety: Three Life Hacks
- What Do You Do When Times Get Tough?
- A Foolproof Formula for Finding Peace During Uncertain Times
- What Will You Do if Your Family and Friends Seem Unsupportive?
- How to Help Elderly Parents Deal With Depression and Anxiety
- What You Need To Do To Have A Fulfilling Retirement
- How To Hire the Best Elderly Care Provider
- What Is Oxidative Stress And Why Is It Bad?
- Four Ways To Incorporate Movement Into Everyday Life
- How To Get Started With Decluttering
- How To Control Issues With Emotional Eating
- 5 Ways to Tackle Social Anxiety
- Symptoms Of A Gluten Intolerance
- How To Stop Worrying All The Time
- Steps To Better Self Development
- New Help for Type 2 Diabetes
- What Being Wrong Teaches You
- 5 Activities That Will Get You Out Of The House
- Conquer Social Anxiety With These 5 Tips to Increase Your Courage
- Offshore Banking for the Average Person
- Time Management: Is It Really Worth the Effort?
- Avoid Being Scammed for Your Money
- How Retirement Affects Cognitive Decline
- The Conscientious Path to Boosting Your Immune System
- New Research for Increasing Your Serotonin Levels
- Your Most Dominate IQ
- Income Options for Retirees
- Cognitive Changes in Seniors as We Age
- About Women: The Challenges Men Don’t Understand
- The Lost Art of Listening
- Playing It Safe With Artificial Sweeteners
- Expand Your Mind: Discover Public Media
- Differences Between Credit Unions and Banks
- About Outlet Malls and How You Can Save More
- What Your Kids Can Teach You About Self-Care
- 5 Cruel Truths That You Need to Know
- Know This About Your Pharmacist
- Silent Heart Attacks and You
- Caffeine Use Disorder
- Living with COPD
- What You Need to Know About Keeping Your Joints Safe and Healthy
- 3 Little Known Truths to Help You Plow Through Tough Times
- Every Credit Card Owner Should Know These Things
- Our Jaunt to the Mainland
- How Seniors Can Navigate Downsizing
- Adventures in Paradise
- “To Age” or “To Mature”
- Retire on a Budget
- 12 FUN RECREATIONAL ACTIVITIES FOR SENIORS
- Life of a Senior Country Hick
- Life is a Routine
- Growing Up Not a Job for Kids
- Who's in Your Corner?
- How to be More Open and Share Your Feelings
- 6 Ways to Strengthen Your Bones as You Age
- Perceived Abuse?
- Getting to Know Him
- Taking a Sensible Approach to Selflessness
- Tips and Tricks for Longevity
- Following God's Plan to Crush Your Goals
- How to Use the Internet to Find Low-Cost Hotel Rates
- Your God of Christmas
- What You Need to Know about Sugar and Your Immune System
- The Benefits of Meditation and Prayer in Everyday Life
- Common Problems Caregivers Face When Working With Seniors
- 8 Ways to Reduce Your Gas Expense
- 7 Ideas to Help You Care Less About What Everyone Thinks
- Tis the Season for Loneliness?
- 13 Simple Ways to Increase Your Energy and Mobility
- Feel Better by Leaving the Burden of Guilt Behind
- How to Overcome Frustration and Disappointment
- The 3 Most Effective Leisure Activities for Preventing Dementia
- Self-Education Habits That Enable You to Teach Yourself Anything
- How Practicing Generosity Helps You Find Happiness
- Surprising Facts about Smoking and Your Mental Health
- Learning How to Become a Good Storyteller
- 7 Low-Carb Hacks to Help You Feel Full All Day
- Tips to Increase Your Energy When You Feel Worn Out
- What Can a Gluten-Free Diet Do For You
- What You Can Do
- How to Eat Healthy During the Holidays
- Finding Peace
- Surprising News about Serotonin and Depression
- Dealing with the Death of a Loved One
- Feeling Lonely?
- Are You a Victim
- The Importance of Looking to the Future
- 5 Ways to Feel Gratitude
- How to Keep Going
- Top 10 Life Secrets
- Long Road Trip 3
- Senior Road Trip 2
- Senior Road Trip 1
- Seniors Make Each Day Count
- 9 Ways to Push Beyond Fear
- Heal Your Broken Heart
- Laugh Your Way to Good Health
- Get a Handle on Your Debt
- Read This Before You Have Laser Eye Surgery
- Learning How to Overcome Failure
- How to Connect with Others
- Dont Get a Prepaid Card
- See How Easily You Can Make
- Time Management vs Energy Management
- Say Goodbye to Daytime Drowsiness
- Top 5 Costs Retirees Often Fail to Foresee
- 5 Dirty Tricks Credit Card Companies Like to Play
- Understanding the Federal Reserve
- Interesting Seniors Memories - 1
- How the Top 1 percent Think
- Stop Seeking Approval from Others
- Beware of Energy Drinks
- 9 Strategies to Boost Your Energy
- Life Long Learning Budget
- A Love Letter
- Don't Believe Everything
- Lying to Yourself
- Stop Procrastinating
- Quit Smoking
- Human Relationships
- Sugar and Salt
- Develop Healthy Habits
- Super Senior Centenarians
- loneliness
- Importance of Mindfulness
- Strengthen Your Health
- Grumpy Old People
- Budget Friendly Travel
- Ways to Relax
- Becoming a Senior Entrepreneur
- Good to Lose Interest
- Seniors and Applesauce
- Eat Healthy food
- Gratitude Improves Health
- 17 Tips to Lose
- Benefits of Relaxing in a Sauna
- Senior Trip to Colorado
- Letting Go of Anger
- An Aging Metabolism
- Aging Well
- About Managing Pain
- Age Gracefully
- Land a Better Fare
- aging grandparents
- Aging Affects Mood
- 10 Ways to Manage Frustration
- 9 Things Emotionally Healthy People Do
- Keep Your Mind Young and Healthy
- Challenges Long Distance Caregiving
- Handle Interference Technology
- About the Farm
- Save Money Travel
- Speed Up Your Metabolism
- Eat Healthier on a Tight Budget
- walking for weight loss
- Essential Senior Superfoods
- Secrets from Seniors on Finding Lasting Love
- Senior's Guide Nutrition
- Senior Guide Strong Hands
- 7 Tips to Maximize Retirement
- Problems Can Sneak Up on Seniors
- GentryBnB
- college prep tips
- What Baby Boomers Should Know
- 15 Healthy Ways to Comfor Yourself
- Senior Online Dating
- Seniors Approaching Birthday
- How to Introduce Your Adult Children to Your Significant Other
- Guide to Healthy Skin
- How to Thrive
- Find Relief from Snoring
- What About Macular Degeneration?
- Vegetarian Path to Healthy Aging
- Dietary Fiber
- Develop Your Creativity
- Need for Validation
- Overcoming Frailty
- Senior Shakeups
- Senior Medication Management
- Quality Senior Sleep
- Empty Nest Syndrome
- Seniors Travel "Locally"
- Senior Travels
- Benefits of Naturopathy
- A Senior's Guide
- Medication Safety Tips
- Losing Weight After 40
- Limited Resources
- Enjoy a Day
- Benefits of Juice Fasting
- Be More Creative
- An Essential Nutrient: Water
- Exercising Strategies to Increase Your Energy
- Ease Chronic Pain
- Cultivate Positive Behavior in Your Teenagers
- lose weight on a plant diet
- Seniors Winter Hawaii
- Love Yourself
- Ways to Bury the Pain From Your Past
- Lower Your Medical Bills
- Working Through Difficult Emotions
- Lessons from Seniors
- Strengthen Your Heart Health
- Counsel for Seniors
- Banish Self Destructive Thoughts
- Why Adult Friendships are Important
- Benefits Juice Fasting
- Seniors with Hearing Loss
- Inner Balance in a Hyper-C0nnected World
- Improve Your Powers of Concentration
- Monthly Financial Survival
- Benefits of Strength Training
- Managing Family Stress
- Handle Toxic Relationship
- What is the Point of Life?
- Top 10 Steps to Enhance Your Memory
- How to Deal With Loss
- 15 Ways to Stay Connected with Your Grandchildren
- Alcohol Ages You
- Coffee and Brain Health
- Surprising Truth About Weight Loss
- Health Benefits of a Vegan Diet
- practicing random acts of kindness
- strategies to help lose weight
- Talking to Strangers
- dementia
- Senior Guide
- Financial Fraud and Seniors
- Staying Brain Sharp
- Boost Our Immune System
- Benefits of Covid
- Essential Communication Skills
- Benefits of Fasting
- The Cab Driver
- Top Ten Benefits of a Daily Walk
- Helping Seniors Prevent Falls
- Thirteen Ways for Seniors to Maximize Immunity
- 10 Anti-Aging Techniques
- Flip House
- Thirteen Natural Ways to Fall Asleep Quickly
- Best Time Seniors Quit Smoking
- Memory Issues?
- A Great Experience!
- Good News!
- Immune System Powerup
- The Human Spine
- Alcohol and Our Brains
- Health Care Needs After Seventy -2
- Our Health Care Needs Beyond Seventy
- inflammation
- From a Friend
- More Benefits of Laugher
- Laughter Benefits Our Bodies
- Mountain Grandeur
- Yellowstone Here We Come!
- Memories and Special People
- Seniors Travel
- Childhood Memories
- Seasons of Life
- Influenza or Pneumonia
- Diabetes
- Respiratory Diseases
- Arthritis
- Heart Disease
- Seniors Oral Health
- Senior Balance Issues
- Senior Health Concerns
- Bouncing Back
- Becoming a Senior
- On Being Content
- Science and Evolution
- Priorities
- 13 Natural Ways to Fall Asleep Quickly
- How to Care for a Loved One Long-Distance
- When Travel Brings a Smile
- What's This About a Vegan Diet?
- GMO, Friend or Foe?
- What If?
- Rest for Seniors
- The Virus, Covid-19
- A Healthy Option?
- Eating Healthy
- Healthy Habits
- Exercise
- The China Study
- Guilt
- Stress Busters
- Is Science Suspect?
- Hope
- Politics and Religion
- When Life Ends
- Bible Biography
- A Wandering Mind
- You Find What You Seek
- About Me
- Privacy Policy
- Contact Me
- What's New?
Diabetes
One of the challenges of becoming a senior is dealing with the reality that our health is not something we can glibly assume that all is OK, as we probably did in our youth. Our health now requires constant monitoring to assure its maintenance or improvement, as the case may be.
Diabetes Statistics
Relevant facts about diabetes include:
- More than 34 million people in the United States have diabetes and 1 in 5 don’t know it.
- More than 88 million adults in the United States have prediabetes and 1 in 5 don’t know it.
- Diabetes is the 7th leading cause of death in the United States.
- Type 2 diabetes accounts for 90% to 95% of all diagnosed cases of diabetes
- Over the last 20 years, the number of cases diagnosed with diabetes has more than doubled as the American population has aged and become overweight or obese.
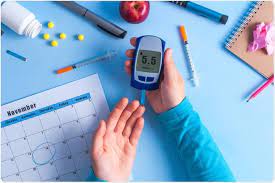
One of the possible threats to our health is diabetes, type 1 or type 2. Diabetes can have severe consequences if not carefully monitored and treated. This article will attempt to address some important issues related to diabetes.
Diabetes is a chronic (long-lasting) disease that affects how your body turns food into energy. There is no cure for diabetes, but with treatment and ongoing self-management strategies, we can live long and healthy lives. Some people do go into remission, thought this is not the same as a cure.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (also known as juvenile or insulin-dependent diabetes), is usually diagnosed in young adults, teens, and children, but it can develop at any age.
Diabetes is more common in males than in females, However, females tend to have more serious complications and face a greater risk of death than males. Why males face a greater risk of getting diabetes than females is unknown, though being overweight is a risk factor.
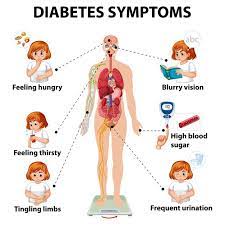
First, let’s look at type 1 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is when our bodies do not make enough insulin. Insulin helps our blood sugar enter the cells where it can be used for energy. Without insulin, blood sugar cannot enter the cells and so builds up in the bloodstream. High blood sugar damages the body and causes many symptoms and complications of diabetes, such as blindness or nerve problems .
Type 1 and type 2 diabetes have similar symptoms. Over time, they can exhibit many of the same complications. Yet, they are very different diseases. With type 1 diabetes, the body is not producing enough insulin on its own. Taking insulin is necessary for survival to take glucose from the bloodstream and move it into the body’s cells.
Type 2 Diabetes
For people with type 2 diabetes, the body’s cells no longer respond well to insulin. We say this is insulin resistance. The body struggles to move glucose into the cells even with adequate levels of insulin. Over time, the body may stop making insulin entirely.
Type 1 diabetes develops very rapidly and the symptoms are very obvious. For type 2 diabetes, symptoms may develop over many years. The person may not even know they have diabetes until a complication develops.

The good news is type 2 diabetes can be prevented. All it takes is proven, achievable lifestyle changes. If we lose some weight and get more physically active we will be less likely to get diabetes.
If you would like to learn your risk of diabetes, take the 1-minute prediabetes risk test. If the test confirms you are prediabetic, you can join a CDC-approved National Diabetes Prevention Program to make lasting changes and learn how to make lasting lifestyle changes to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
Here is a guide to help you prevent type 2 diabetes.
Return to SeniorHealthyLifestyles.com home page.
Please share your thoughts and any response you may have in the form below.